How AI Works : From Data Processing to Model Deployment
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad field of study encompassing a wide range of technologies and approaches. While there is no single definition of AI that is universally agreed upon, it is generally understood to be the ability of machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving.
AI is made possible by a variety of techniques and algorithms, including:

Machine learning:
Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. This is done by training algorithms on large datasets of examples, allowing them to identify patterns and relationships in the data.
Natural language processing (NLP):
NLP is a field of AI that deals with the interaction between computers and human language. NLP algorithms can be used to understand and generate human language, translate languages, and extract information from text.
- Understanding Words: NLP starts with computers reading or listening to human language. It’s like teaching a computer to understand words and sentences, just as we do.
- Figuring Out Meaning: The computer then tries to figure out what these words mean together. This step is like solving a puzzle, where the computer learns the meaning behind words and phrases.
- Responding in Language: Next, NLP helps the computer to respond. This could be writing a reply or speaking out an answer. It’s like teaching the computer to talk or write back to us.
- Translating and Finding Info: Finally, NLP lets computers translate between different languages or find specific information in a lot of text, like a super-smart language detective.
In short, NLP is all about making computers understand and use human language, turning them into language experts in their own digital way!

Computer vision:
Computer vision is a field of AI that enables computers to interpret and understand visual information from cameras and other sensors. Computer vision algorithms can be used to identify objects, track movements, and generate descriptions of images.
- Seeing: Computer vision begins with computers receiving images or videos, much like how our eyes see things. This visual information comes from cameras or sensors.
- Recognizing and Understanding: Next, the computer analyzes these visuals to identify objects and understand what’s happening in them. It’s like playing a game of ‘I Spy’ where the computer learns to spot different things, like cars, people, or animals.
- Interpreting and Responding: Finally, the computer uses what it sees to make decisions or descriptions. This could be anything from describing a photo, recognizing a face, or even understanding the actions in a video.
In essence, computer vision is about teaching computers to ‘see’ and make sense of the world through images, much like how we use our eyes to understand our surroundings.
Robotics:
Robotics is a field of AI that deals with the design and operation of robots. Robots are machines that can sense their environment and take action to achieve specific goals. AI is used to control robots and make them more intelligent and adaptable.
- Building and Sensing: First, robots are built with sensors and parts that allow them to sense their environment, much like how we use our senses to understand the world around us. These sensors help the robot to ‘see’, ‘hear’, and ‘feel’.
- Making Decisions: Robots, powered by AI, use the information they get from their sensors to make decisions. This is like how we think and decide what to do next based on what we see and hear.
- Acting and Adapting: Finally, robots act on these decisions. They
- can move, perform tasks, and even interact with people or other machines. The AI in robots helps them adapt to new situations, learning from experience just like we do.
In short, robotics is all about creating smart, adaptable machines that can sense, decide, and act, enhancing their capabilities to assist, work, and even collaborate with us in various aspects of life.
AI is a rapidly evolving field, and new techniques and algorithms are constantly being developed. As AI continues to develop, it is likely to have an even greater impact on our lives, work, and society.
Here is a simplified overview of how AI works from Data Processing to Model Deployment:
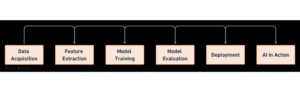
- Data Acquisition: AI systems start with data, which can be text, images, audio, or other forms of information. This data is then processed and prepared for analysis.
- Feature Extraction: The next step is to extract features from the data. Features are the key characteristics of the data that are relevant to the task at hand. For example, in image recognition, features might be the edges, colors, and shapes of objects in an image.
- Model Training: Once features have been extracted, the AI system trains a model. A model is a set of instructions that tells the system how to make predictions or decisions based on the data it has seen.
- Model Evaluation: After the model has been trained, it is evaluated to see how well it performs on new data. This helps to ensure that the model is generalizing correctly and not simply memorizing the training data.
- Deployment: Once the model has been evaluated and found to be satisfactory, it is deployed into production. This means that it is used to make predictions or decisions in real-world applications.
AI is a complex field with many different approaches and techniques. However, the general principles outlined above provide a basic understanding of how AI systems work.
Conclusion
To sum it up, AI is like a smart helper that learns to do tasks by looking at a lot of examples. Here’s in easy steps:
- Collecting Data: AI starts by gathering information, like pictures, words, or sounds. This is like collecting ingredients for a recipe.
- Picking Out Important Bits: Next, AI looks for special bits in the data. For example, in a photo, it might look for shapes and colors.
- Training the AI: Now, AI learns from the data. It’s like teaching it to recognize patterns or understand what the data means.
- Testing the AI: After learning, AI is tested with new data. This is to make sure it has really learned and can handle new situations.
- Using the AI: Finally, the AI is ready to work in the real world. It can help make decisions or predictions based on what it has learned.
So, AI is a bit like going to school. First, you learn from books and teachers, then take tests to see how much you’ve learned, and finally, you use that knowledge in real life. AI does the same with data and learning!